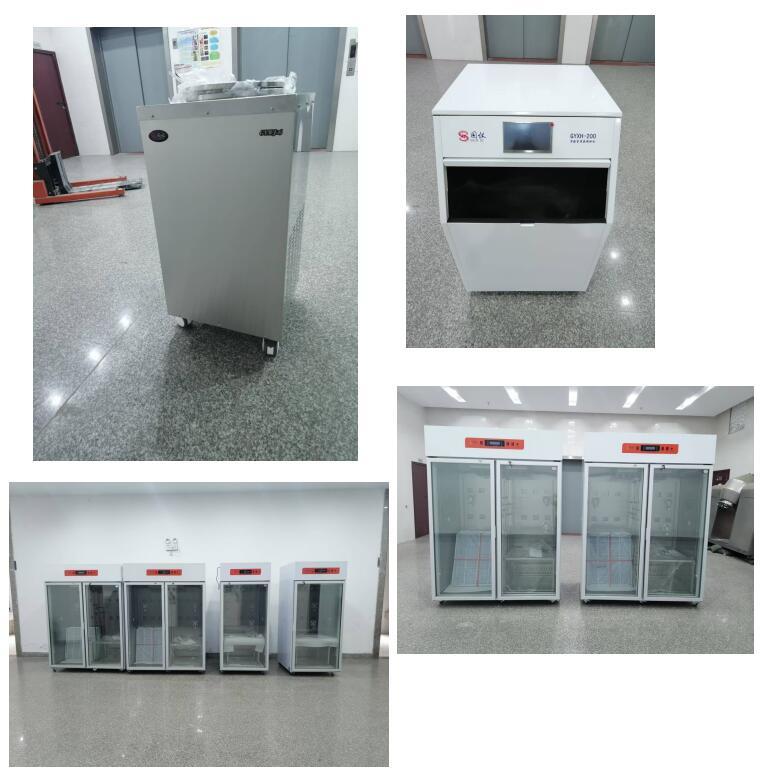
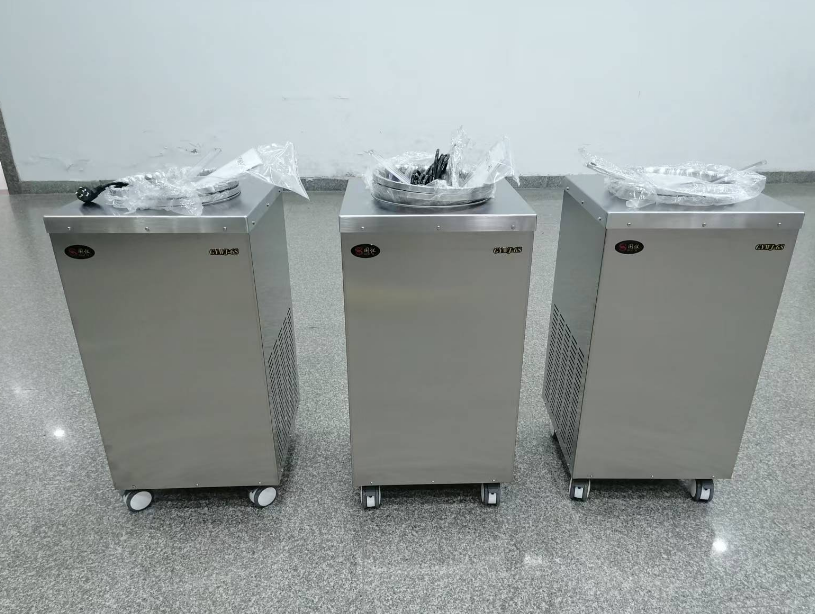
All raw materials and components for our products are sourced from well-known brands in the industry
Focusing on the R&D and production of scientific instruments, supporting software, and reagent consumables
Dedicated to the full-process business of scientific instruments, supporting software, and reagent consumables. From cutting-edge technology R&D to standardized manufacturing, and then to broad market sales, we provide one-stop product supply and technical support services for customers in various fields, relying on deep industry experience and innovative spirit.
About laboratory lce Maker
About Chromatography Refrigerator
About Surgical Slush Machine
About Laboratory Refrigerators and Freezer
About centrifuges
Basic Knowledge and Application
Expert Research on Instrument Software & Consumables
Intelligent Manufacturing: Cornerstone of Scientific Research and Innovation
The company's founding team has over 10 years of industry experience, a thorough understanding of laboratory equipment, and a relatively accurate grasp of customer needs. In terms of manufacturing technology, we have core personnel with over 25 years of experience in mechanical and electronic technology. Our circuit control systems are independently developed and hold multiple patents, providing strong technical assurance for customer applications

Qualifications and Certificates
exporting country

Partners

Company Founded In
Why Choose Us

R&D and Innovation
R&D and innovation are the core drivers of sustainable enterprise development

Reliable Quality
Multiple inspection processes are strictly controlled at every level, forging reliable quality

Manufacturing
Improve production efficiency, reduce production costs, and enhance product quality

Sales Management
Precise execution and efficient control of sales activities

Comprehensive After-sales Service
Professional after-sales service to safeguard your processes
News and Information
2025-03-28
Main products: laboratory equipment, laboratory ice makers, centrifuges, drug refrigerators, laboratory chromatography cabinets
Years of industry experience, solving your worries